Practicing with high-quality Next Generation and NCLEX-style sample questions is the most effective way to prepare for the exam, because if practice feels like the actual exam, then the real thing will feel like practice.
Check out our free NCLEX sample questions below!

We are committed to providing you with only the best questions and explanations. Our NGN practice questions include the same hallmark features that have helped over a million nurses succeed – clinically-relevant content, vivid imagery and illustrations, and in-depth explanations for correct and incorrect answers.
Our learn-by-doing philosophy is paired with industry-leading illustrations to help you retain more information in less time.
Our team of experts writes detailed rationales for each answer choice so you can learn why you got an answer right or wrong.
Set up custom tests to hone in on your weaknesses and turn them into strengths with our "Create Test" feature.
The best way to become more familiar with NCLEX-style questions is by practicing them. You’ve been through nursing school, so you have the knowledge. Now you just need to apply it. Choose your exam below to answer a few exam style questions …
NCLEX-RN Sample Questions NCLEX-PN Sample Questions NCLEX-RN Sample QuestionsThe questions on the NCLEX-RN are designed to test your critical thinking skills and ability to apply knowledge in real-world scenarios. Don’t waste time practicing low-level questions! Challenge yourself with our NCLEX-RN sample questions.
The nurse is caring for a client at 39 weeks gestation who is receiving an IV oxytocin infusion for induction of labor. The nurse notes recurrent late decelerations on the fetal monitor. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? Select all that apply.
| 1. Administer an IV fluid bolus |
| 2. Apply abdominal vibroacoustic stimulation |
| 3. Discontinue the IV oxytocin infusion |
| 4. Prepare the client for an amnioinfusion |
| 5. Reposition the client laterally |
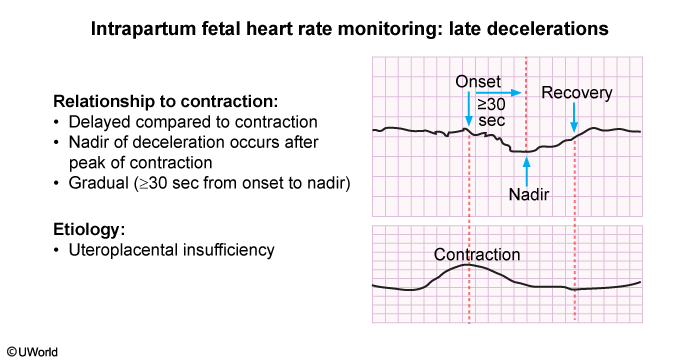
A late deceleration is a gradual decrease in fetal heart rate (FHR) with a uterine contraction that reaches its lowest point (ie, nadir) after the contraction’s peak with a slow return to baseline. Late decelerations occur as a reflexive chemoreceptor response to temporary fetal hypoxemia or fetal metabolic acidemia (in severe cases). Uteroplacental insufficiency, uterine tachysystole, and maternal supine hypotension are common causes because they compromise perfusion and oxygen availability to the fetus.
Intrauterine resuscitation interventions to improve fetal perfusion and oxygenation include:
The mnemonic VEAL CHOP helps recall of causes of FHR changes on monitor tracings.
(Option 2) Vibroacoustic stimulation is used during nonreactive nonstress tests (ie, no accelerations) to provoke fetal movement, which helps determine whether the absence of expected accelerations is physiologic (eg, fetal sleep cycle) or pathophysiologic (ie, fetal acidemia). It is never performed during FHR decelerations or fetal bradycardia.
(Option 4) An amnioinfusion is indicated to relieve persistent, recurrent variable decelerations caused by umbilical cord compression. It is not indicated for late FHR decelerations or uterine tachysystole.
Educational objective:
Late decelerations of fetal heart rate indicate compromised fetal oxygenation and perfusion. Intrauterine resuscitation interventions include administering an IV fluid bolus, discontinuing the IV oxytocin infusion, and repositioning the client laterally.
The nurse is delegating client care tasks to a licensed practical nurse (LPN) and unlicensed assistive personnel. Which of the following assignments are most appropriate to assign to the LPN? Select all that apply.
| 1. Administer a client’s daily dose of subcutaneous insulin glargine |
| 2. Administer a scheduled oral analgesic to a 2 days postoperative client |
| 3. Complete an admission nursing interview for a client admitted for elective hysterectomy |
| 4. Reinforce teaching on self-administration of insulin to a client with diabetes mellitus |
| 5. Tally the shift’s intake and outputs for the entire unit |
*Limited assessments (eg, lung sounds, bowel sounds, neurovascular checks).
LPN = licensed practical nurse; LVN = licensed vocational nurse; RN = registered nurse; UAP = unlicensed assistive personnel.
Nurses preparing to delegate client care to a licensed practical nurse (LPN) and/or unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) should consider the 5 rights of delegation. The LPN can monitor and care for stable clients who have been initially evaluated by a registered nurse (RN). Interventions LPNs may perform include:
(Option 3) Performing admission or initial assessments is outside the scope of the LPN and UAP. The RN must perform initial assessments in order to analyze the findings and formulate the client’s plan of care before delegating tasks.
(Option 5)The LPN is capable of performing routine care (eg, calculating daily intake and output, toileting). However, the UAP may also perform these tasks, which frees the LPN to perform more complex duties. Therefore, the most appropriate staff member to assign the task of calculating intake and output to is the UAP.
Educational objective:
Nurses preparing to delegate client care should consider the 5 rights of delegation. Appropriate tasks to delegate to a licensed practical nurse include administration of oral and parenteral medications, excluding IV route, and reinforcement of teaching previously provided by the registered nurse.
The nurse cares for a client with aortic stenosis who was admitted due to syncope on exertion and dyspnea. Identify the area where the nurse would best auscultate the client’s heart murmur.
Think of a location on the image which you deem right and click on ‘Show Correct Regions’ link to see if your selection is correct.
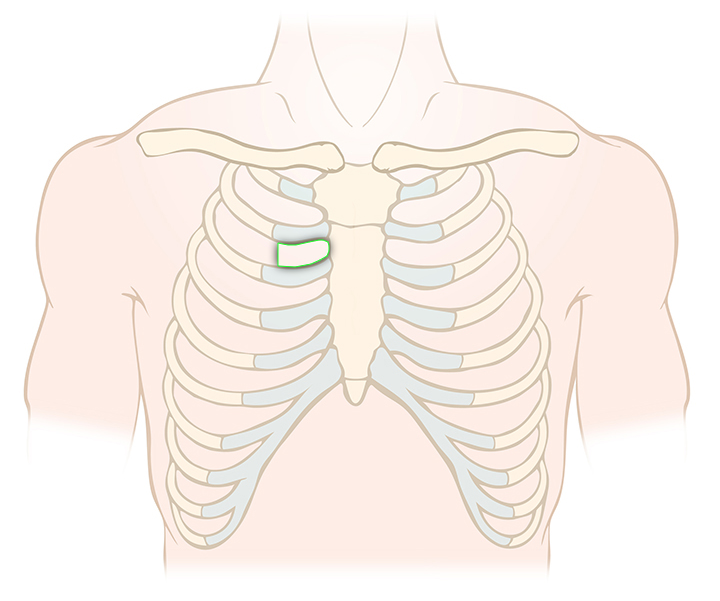
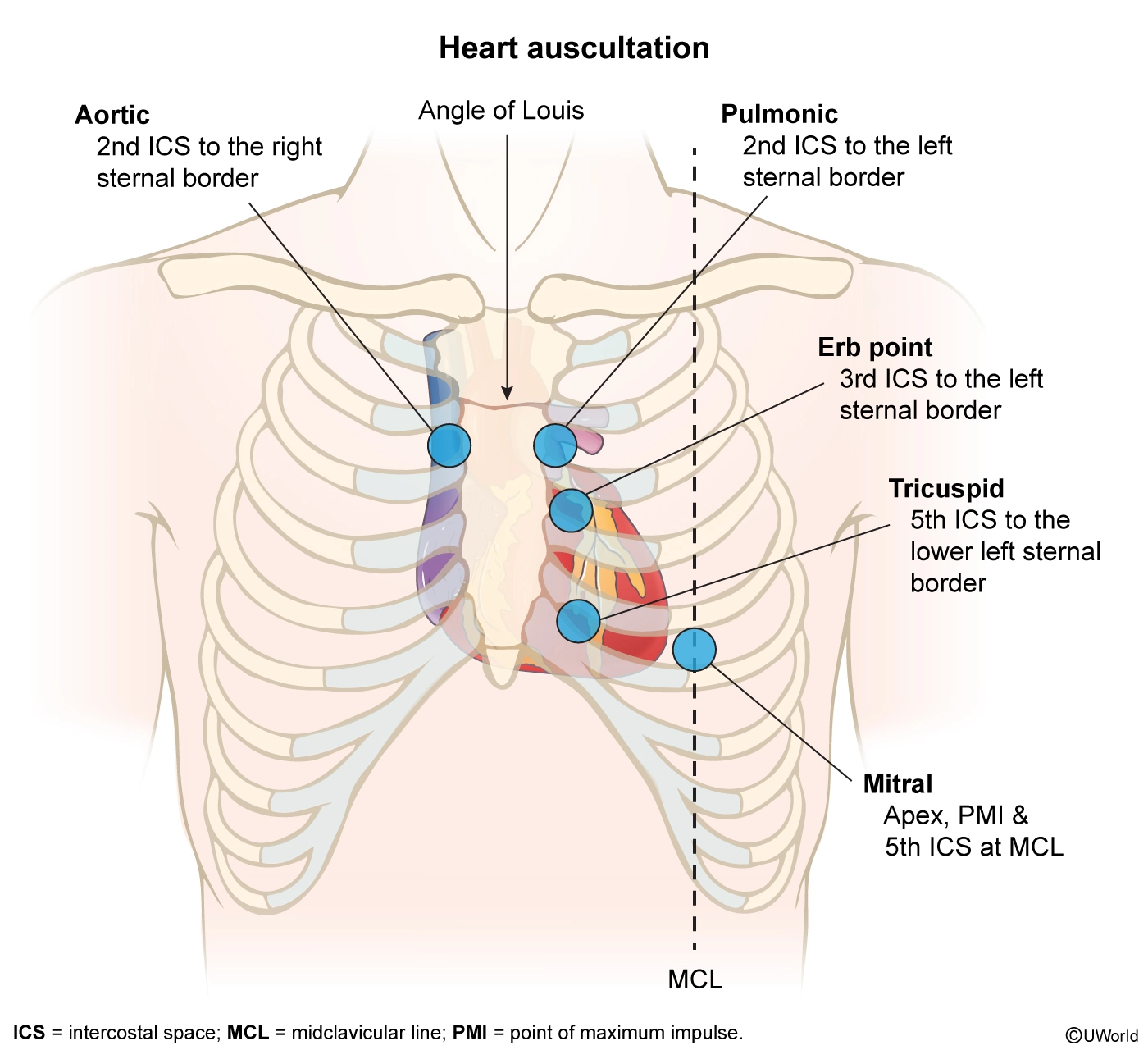
Aortic stenosis (AS) is a type of valvular heart disease characterized by narrowing of the aortic valve opening, which limits the left ventricle’s ability to eject blood into the aorta. AS may occur from hardening (ie, calcification) of the valves, congenital heart disorders, or inflammation. If left untreated, AS may result in heart failure and pulmonary hypertension as compensatory mechanisms fail.
When assessing a client with AS, the nurse should auscultate in the aortic area (ie, second intercostal space at the right sternal border) for a loud, systolic ejection murmur heard following the first heart sound. The aortic area, rather than directly over the heart valve, is the preferred location for auscultation as the heart sounds travel in the direction the blood flows. Additional clinical manifestations of aortic stenosis include chest pain, shortness of breath, and/or syncope that are worsened by exertion.
Educational objective:
Aortic stenosis is a type of valvular heart disease causing narrowing of the valve between the left ventricle and aorta, impairing ejection of blood from the heart. Nurses attempting to auscultate heart murmurs associated with aortic stenosis should listen at the right sternal border, second intercostal space (ie, aortic area).
A health care provider prescribes cefuroxime 30 mg/kg/day PO divided in equal doses every 12 hours for a child with a urinary tract infection. The child weighs 34 lb. Based on the available concentration of cefuroxime, how many mL would the nurse administer per dose? Click the exhibit button for additional information. Record your answer using one decimal place.
Correct Answer: 4.6 mL

Using dimensional analysis, the following steps are performed to calculate the volume of cefuroxime per dose in milliliters:
Educational objective:
To calculate the volume of cefuroxime in milliliters per dose, the nurse should first identify the prescribed dose (eg, 30 mg/kg/day) and available medication (eg, 250 mg/5 mL) and then convert to volume in milliliters per dose (eg, 4.6 mL).
Alternative Method:
The formula method is an alternate way to calculate medication dosages. However, this method may increase the occurrence of miscalculation and medication errors. If you choose to use this method, do not round calculations until the final step.
Using the formula method, the following steps are performed to calculate the volume of cefuroxime per dose in milliliters:
The nurse receives new prescriptions for a client with right lower quadrant pain and suspected acute appendicitis. Which prescription should the nurse implement first?
| 1. Administer 0.25 mg hydromorphone IV push for pain |
| 2. Draw blood for complete blood count and electrolyte levels. |
| 3. Initiate IV access and infuse normal saline 100 mL/hr |
| 4. Obtain urine specimen for urinalysis |
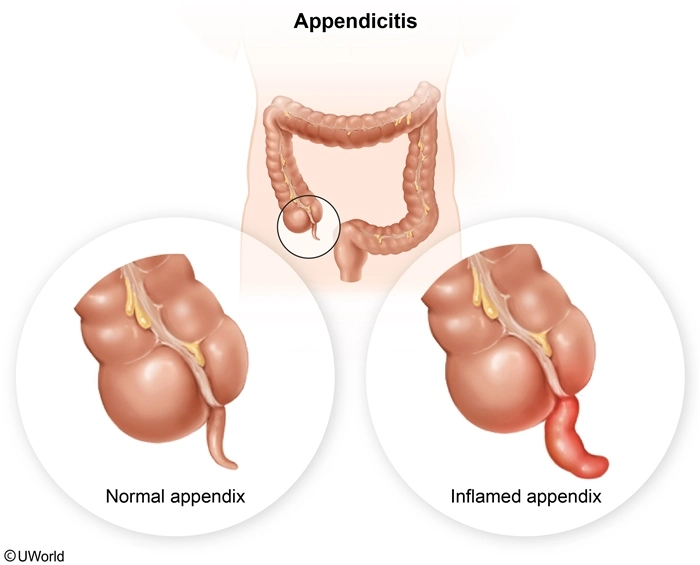
Appendicitis is inflammation of the appendix and often results from obstruction by fecal matter. Appendiceal obstruction traps fluid and mucus typically secreted into the colon, causing increased intraluminal pressure and inflammation. As appendiceal intraluminal pressure and inflammation increase, blood circulation to the appendix is impaired, resulting in swelling and ischemia. These factors increase the risk for appendiceal perforation, a medical emergency, which may lead to peritonitis and sepsis.
When prioritizing care of the client with appendicitis, the nurse should utilize the ABCs (ie, airway, breathing, circulation). Fluid resuscitation with IV crystalloids (eg, normal saline, lactated Ringer solution) is an important intervention aimed at preventing circulatory collapse resulting from fluid losses (eg, vomiting, diarrhea) and NPO status (Option 3).
(Option 1) Pain medications may be administered to promote comfort, but should be administered via IV route to maintain NPO status in case of emergency surgery. However, circulation takes priority over pain medication.
(Options 2 and 4) Blood and urine samples often are prescribed to assist with treatment and care decisions. However, the nurse should prioritize circulatory status over obtaining laboratory specimens.
Educational objective:
Nurses caring for clients with appendicitis should prioritize client care according to the ABCs (ie, airway, breathing, circulation). Initiating IV crystalloids (eg, normal saline) is a priority action that prevents circulatory collapse resulting from fluid losses (eg, vomiting, diarrhea) and NPO status.